
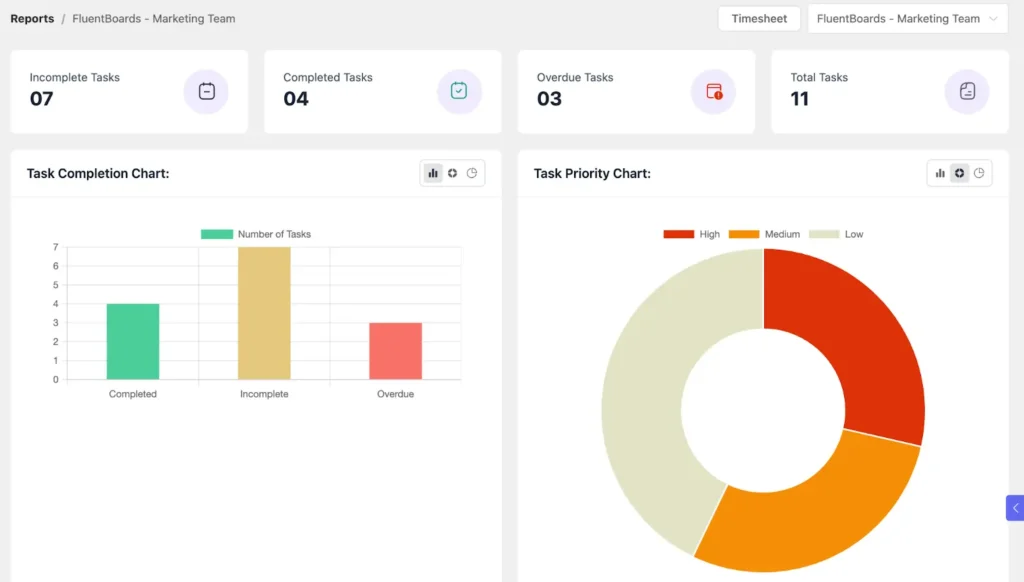
Project Management KPIs: Key Metrics to Track, Measure, & Optimize to Guarantee Project Success
Imagine you’re a captain steering a ship without a compass! Where would you end up?
Sure, you might somehow reach your destination, but one thing is certain – chaos!
The importance of Project Management KPIs in project management is exactly the same. They act as your project’s compass, guiding you with real-time insights:
- Are you on track?
- What’s working?
- What needs improvement?
But with so many KPIs out there, how do you know which ones matter and what they’re for?
Keep scrolling to find your answers!
What Are Project Management KPIs?
Project Management KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are numbers or data points that show how well a project is doing. They help track progress, budget, deadlines, and team performance, making it easier to see if everything is on the right track.
These metrics give project managers clear insights into what’s working and what needs improvement. Some KPIs focus on numbers, like cost and time, while others measure things like client or team satisfaction.
Types of Project KPIs
Not all project management KPIs come in a pure number format. And based on how they present results, we can segment these KPIs into three groups –
- Quantitative KPIs: These are straightforward metrics with numeric values like budget variance, schedule variance, subtask completion rate, etc.
- Qualitative KPIs: These KPIs rely on subjective insights, usually collected through surveys or assessments. Example – team satisfaction, client satisfaction, stakeholder engagement, etc.
- Mixed-Format KPIs: These combine measurable data with qualitative insights.
On the other hand, based on the aspects of the project they measure, we can categorize them into the following groups:
- Progress & performance KPIs: Planned vs. actual progress, Subtask completion rate, WIP limit
- Budget & cost management KPIs: Budget variance (BV), Cost performance index (CPI), Return on investment (ROI)
- Timeline & efficiency KPIs: Schedule variance (SV), Schedule performance index (SPI)
- Team & stakeholder KPIs: Employee churn rate, Net promoter score (NPS)
- Quality & risk management KPIs: Risk exposure
Leading KPIs vs. Lagging KPIs
Leading KPIs are predictive indicators that help forecast future outcomes. They allow you to take proactive steps before issues arise.
Examples:
- Task completion rate
- Employee churn rate
- Team workload balance
Lagging KPIs measure past performance, showing results after they’ve happened. These help assess success but don’t allow for immediate course correction.
Examples:
- Project completion time
- Budget variance
- Customer satisfaction score
Why Project Management KPIs Matter?
Let’s get straight – proper project management is important for the success of your project, while to keep your project management journey on track, you need the help of project management KPIs.
With the right KPIs in place, project management becomes more strategic, predictable, and efficient. Here’s why project management KPIs are so important:
- Keep you on track: By assessing your overall project to-do list, KPIs help determine whether a project is progressing as planned (meeting goals and deadlines) or if adjustments are needed.
- Spot problems & risks early: KPIs help identify both visible and hidden challenges. They alert you early if things are off track and highlight potential risk factors, allowing you to make adjustments before it’s too late.
- Supports smarter decisions: They prevent you from making blind guesses. Instead, they enable you to make well-informed decisions based on real-time insights and guide your team through every project phase like an experienced captain.
- Boosts team performance: KPIs make expectations clear for everyone involved. And when teams know exactly what they need to achieve, both individually and collectively, they stay focused and deliver results more efficiently.
- Makes team management easy: With precise data on who is doing what, assessing individual performance, identifying shortcomings, and managing project team becomes smoother than ever.
- Measures success: You need data to determine whether your project was a success, and KPIs provide that. Whether it’s staying within budget or delivering quality work, KPIs help measure your project’s success.
- Optimizes resources: KPIs help track resource utilization, allowing you to allocate time, budget, and team roles and responsibilities more effectively.
12 Essential Project Management KPIs and How to Calculate Them
There are various project management KPIs that project managers rely on to keep their projects on track. The most important KPIs for you will depend on your project type, specific needs, and the aspects of the project you want to focus on.
Let’s explore the key KPIs of project management that truly matter!
Planned vs. Actual progress / Progress Variance (PV)
Planned vs. Actual Progress measures how your project’s current status compares to the initial plan. This data helps project managers determine:
- How far the project has progressed compared to the original goals
- How many tasks are completed on time
- What adjustments are needed to keep the project on track and ensure timely completion
Ways to calculate progress variance (PV)
Modern project management tools can be incredibly useful for tracking this metric. In fact, some of these tools allow you to easily identify which project phases or stages have the most overdue tasks.
However, if you want to calculate it manually, then use this formula –
Progress Variance = {(Actual Progress−Planned Progress) / Planned Progress} ×100
Note: A negative variance (-25%) will mean the project is behind schedule, while a positive variance will indicate it’s ahead of schedule.
Subtask Completion Rate
When working on a large project, the sub-task completion rate is an important metric for keeping everything on track. By analyzing this data, you:
- Ensure your overall project is progressing in a strategic manner
- Don’t let any tasks be left behind
- Identify sub-tasks that are delaying the completion of a particular task and take action accordingly
Ways to calculate subtask completion rate
Modern project management tools provide real-time tracking of sub-task completion, helping teams visualize which minor tasks are lagging behind.

If you prefer to calculate it manually, use this formula:
Subtask Completion Rate = (Completed Subtasks/ Total Subtasks) × 100
For example, if a task has 10 sub-tasks and 8 are completed, the completion rate would be:
- (8/10) × 100 = 80%
Note: A low percentage may indicate bottlenecks that need immediate attention
Work in Progress (WIP) Limit
This is a key project management metric that controls the number of tasks actively being worked on at a given time.
It ensures teams focus on completing tasks before taking on new ones, preventing bottlenecks and improving workflow efficiency.
WIP Limit –
- Reduces task overload and improves productivity
- Prevents multitasking, ensuring high-quality work
- Identifies bottlenecks in the project workflow
- Speeds up task completion by promoting a smooth flow of work
How to set an effective WIP Limit
- Assess how many tasks your team can handle efficiently at once.
- Identify the number of tasks currently in progress and how long they take to complete.
- Keep the WIP limit low enough to prevent overload but high enough to maintain steady progress.
- Continuously review and refine the WIP limit to optimize efficiency.
Example: If a development team has 5 members and each can handle 2 tasks at a time, the ideal WIP limit would be 10 tasks. If the limit is exceeded, new tasks should not be started until ongoing ones are completed.
Level up your WordPress project management game with this Trello equivalent solution – where limitless possibilities come at an unbeatable price!
Schedule Variance (SV)
Schedule Variance (SV) helps measure whether a project is ahead of or behind its planned timeline. It compares the earned value (EV) of completed work to the planned value (PV), showing how much progress has been made relative to expectations.
It –
- Helps identify delays early, allowing corrective actions
- Provides insight into whether project milestones are being met
- Ensures better resource allocation and scheduling adjustments
Ways to calculate schedule variance (SV)
SV= EV(Earned value) −PV (Planned value)
Suppose a project has a planned value of $50,000 by a certain date, but the actual earned value of completed work is $40,000.
So, here the SV will be = 40,000−50,000=−10,000
Note: SV > 0 = the project is ahead of schedule, SV < 0 = the project is behind schedule, SV = the project is exactly on schedule
Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) measures how efficiently a project is progressing compared to the planned schedule. It helps project managers assess whether a project is ahead, on track, or behind schedule.
How to calculate SPI
SPI= Earned Value (EV) / Planned Value (PV)
Here,
- Earned Value (EV) = The budgeted cost of work actually completed
- Planned Value (PV) = The budgeted cost of work planned to be completed
Suppose, a project has an Earned Value (EV) of $50,000 and a Planned Value (PV) of $60,000.
So, here the SPI is, 50,000 / 60,000=0.83
Note: If SPI is equal to 1, the project is on schedule. When SPI > 1.0, the project is ahead of schedule. And, when SPI < 1.0, the project is behind schedule.

Step into the Future of Project Management!
Budget Variance (BV)
Budget Variance (BV) measures the difference between the planned budget and the actual costs incurred during a project. It helps project managers assess financial performance and identify whether a project is over or under budget.
This KPI helps project managers:
- Track how well the project stays within the allocated budget.
- Identify cost overruns early and take corrective action.
- Improve future budgeting by analyzing trends and past variances.
Ways to calculate budget variance (BV)
The formula for Budget Variance is:
BV = Planned Budget − Actual Cost
For example, if a project’s planned budget is $50,000, but the actual cost incurred is $55,000, the budget variance would be:
- BV=50,000−55,000=−5,000
This means the project is $5,000 over budget, requiring a review of expenses to avoid further overspending.
Note: Positive BV (+) indicates the project is under budget, negative BV (-) Indicates the project is over budget and zero BV (0) means the project is exactly on budget.
Cost Performance Index (CPI)
CPI is a crucial financial metric in project management that evaluates whether the project is staying within its financial limits or exceeding costs.
It helps project managers understand:
- How efficiently costs are being managed
- Whether the project is under or over budget
- The need for financial adjustments to maintain profitability
Ways to calculate cost performance index (CPI)
To calculate CPI, use this formula –
CPI = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC)
- Earned Value (EV): The budgeted cost of completed work
- Actual Cost (AC): The total amount spent on that work
For instance, if a project has an EV of $40,000 and an AC of $50,000, the CPI is = 40,000 / 50,000 = 0.8
Note: CPI > 1.0 means the project is cost-efficient, CPI = 1.0 means the project is on budget, and CPI < 1.0 indicates the project is over budget and needs cost adjustments.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Measuring the financial gain of a project is crucial, and ROI helps determine whether the effort and resources put into a project are paying off.
It compares the net profit gained from a project against its total cost, showing how effectively investments are being utilized.
A high ROI signifies strong financial performance, while a low or negative ROI indicates potential inefficiencies or losses.
Ways to calculate ROI
ROI= {(Net Profit from Project − Project Cost) / (Project Cost)} ×100
So, if a project generates $250,000 in revenue while costing $150,000, the ROI would be:
- {(250,000−150,000) / 150,000)} ×100= 66.67%
This indicates a 66.67% return, meaning the project has been financially beneficial.
Net Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin evaluates a project’s profitability by measuring how much of the total revenue turns into actual profit after deducting all expenses.
By evaluating these metrics, the project manager –
- Understands how efficiently resources are used to generate profit
- Assess the financial health of a project
- Makes better cost-related decisions for future projects
How to calculate net profit margin
Net Profit Margin =(Net Profit / Total Revenue) ×100
Here,
- Net profit = Total revenue – Total expenses
Let’s say a company is managing a software development project. Their total revenue from the project is $200,000 and total expenses are $150,000
So, here the net profit is, $200,000− $150,000 = $50,000
And the net profit margin of this software company is – ($50,000 / $200,000) × 100=25%
Note: A higher net profit margin means the project is financially successful while a lower or negative margin suggests cost inefficiencies.

FluentRoadmap Comes Free with FluentBoards Pro!
Employee Churn Rate
Employee Churn Rate measures the percentage of employees who leave an organization or project team within a specific period.
This KPI is crucial for understanding workforce stability and identifying potential issues in employee retention.
Here’s how it helps –
- High churn can lead to productivity loss and increased hiring/training costs
- It helps identify underlying workplace issues like dissatisfaction, burnout, or poor management
- Maintaining a low churn rate ensures continuity and expertise retention within the team
How to calculate employee churn rate
Churn Rate=(Employees who left during a period/ Total employees at the start of the period)×100
Let’s say, a project team had 50 employees at the start of the quarter. By the end of the quarter, 5 employees left.
So the churn rate would be – (5/50)×100=10%
Note: If the churn rate is under 5%, it indicates a stable and satisfied workforce, while the churn rate over 10% signals potential management or cultural issues that need immediate attention.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a widely used metric that measures customer loyalty and satisfaction based on their likelihood to recommend a product, service, or company to others. It provides insight into overall customer sentiment and brand advocacy.
How to Calculate NPS
NPS = %Promoters − %Detractors
NPS is calculated by asking customers – on a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service to a friend or colleague?
Based on responses, customers are categorized into three groups:
- Promoters (9-10): Loyal customers who actively recommend your brand
- Passives (7-8): Satisfied but not enthusiastic enough to promote
- Detractors (0-6): Unhappy customers who may spread negative feedback
Note: Positive NPS (>0), Negative NPS (<0)
Risk Exposure
Every project comes with risks, and Risk Exposure helps quantify their potential impact. It measures the likelihood of a risk occurring and the potential damage it could cause to the project.
How to Calculate Risk Exposure
The formula for calculating risk exposure is:
Risk Exposure=Probability of Risk × Potential Impact
Here,
- Probability of risk = The likelihood of the risk occurring (expressed as a percentage)
- Potential Impact = The estimated financial or operational damage if the risk occurs
Example: If there’s a 30% chance of a project delay that could cost $10,000, the Risk Exposure would be:
0.30×10,000=3,0000
This means the project faces a potential $3,000 risk impact, and steps should be taken to minimize it.
How to Select the Right Project Management KPIs
Not all KPIs will be relevant to every business or project. The key to selecting the right ones is to focus on metrics that align with your project goals, industry needs, and team workflow.
Here’s how to decide:
1. Define your objectives
Start by identifying your project’s primary goals. Are you aiming to improve efficiency, stay within budget, or enhance team collaboration? Your KPIs should directly reflect these priorities.
For example, if your goal is profitability, focus on Net Profit Margin, Return on Investment (ROI), or Cost Performance Index (CPI). And, if your goal is customer retention, then track Net Promoter Score (NPS)!
2. Identify key performance areas
Break down your project into critical areas such as cost, schedule, quality, team productivity, and risk management. Each area should have specific metrics that help evaluate performance.
3. Choose actionable and measurable metrics
A good metric provides clear, quantifiable data that enables decision-making. Avoid vanity metrics that look impressive but offer little actionable insight.
4. Balance leading and lagging indicators
Leading indicators (like task completion rate) help predict project outcomes while lagging indicators (like ROI) measure past performance. A balanced mix ensures a proactive and reflective approach.
5. Use real-time tracking
Modern project management tools allow real-time tracking of key metrics, helping teams stay agile and make quick adjustments when needed. Select metrics that can be consistently monitored and updated.
6. Avoid overloading with too many metrics
While data is valuable, tracking too many metrics can lead to confusion and inefficiency. Focus on a core set of meaningful metrics that provide the most value to your project.
7. Regularly review and adjust metrics
As projects evolve, some metrics may become less relevant. Periodically review your selected metrics to ensure they still align with project objectives and adjust as necessary.
Track, Measure, Optimize & Succeed!
Project management is a long-term journey – no shortcuts, no magic formulas!
Success comes from strategic planning, staying aligned with objectives, and making data-driven decisions. That’s where project management KPIs come in! They keep you on track, signal when adjustments are needed, and help you anticipate risks before they arise.
So, know your numbers, analyze them, and make informed decisions. We hope this blog post becomes a valuable asset in your next project management endeavor.
That’s all for today! Wishing you a more informed and effective project management journey ahead!
Let’s redefine project management with FluentBoards!
Get Tips, Tricks, & Updates
We won’t send you spam.















Leave a Reply