FluentBoards integrates with Amazon S3, allowing you to store media files, improving your site’s loading speed, and managing storage more efficiently.
This guide will walk you through how you can set up Amazon S3 with FluentBoards.
Get the Amazon S3 account Credentials #
Before anything else, make sure you have an Amazon AWS account set up. You’ll need the necessary credentials to connect S3 with FluentBoards.
Creating an S3 Bucket #
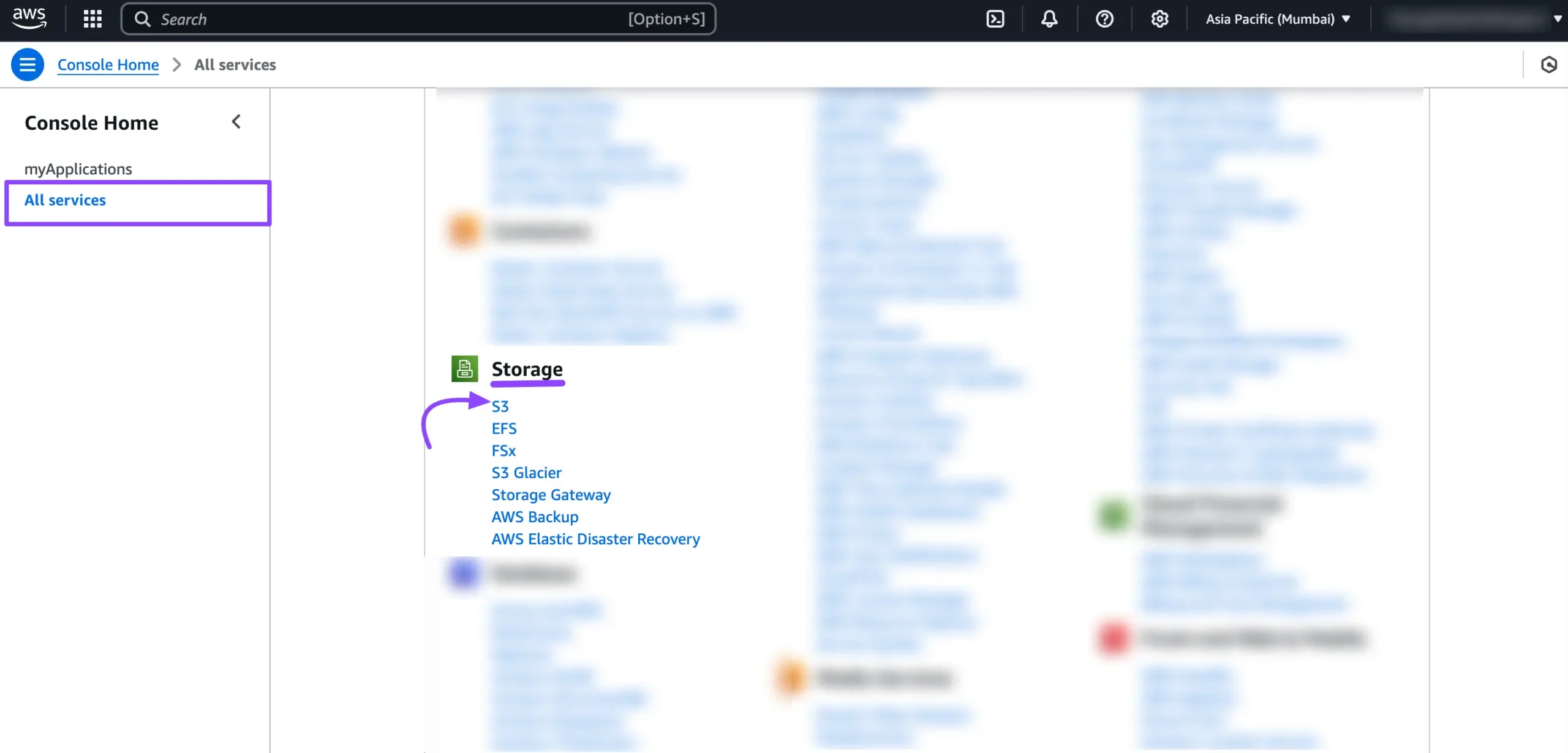
To get started with Amazon S3, log in to your Amazon AWS account. From the Dashboard, click on All Services in the left sidebar. A full list of AWS services will appear here. Now, scroll down to the Storage section and select S3 to proceed.
Choose your S3 Bucket Region #
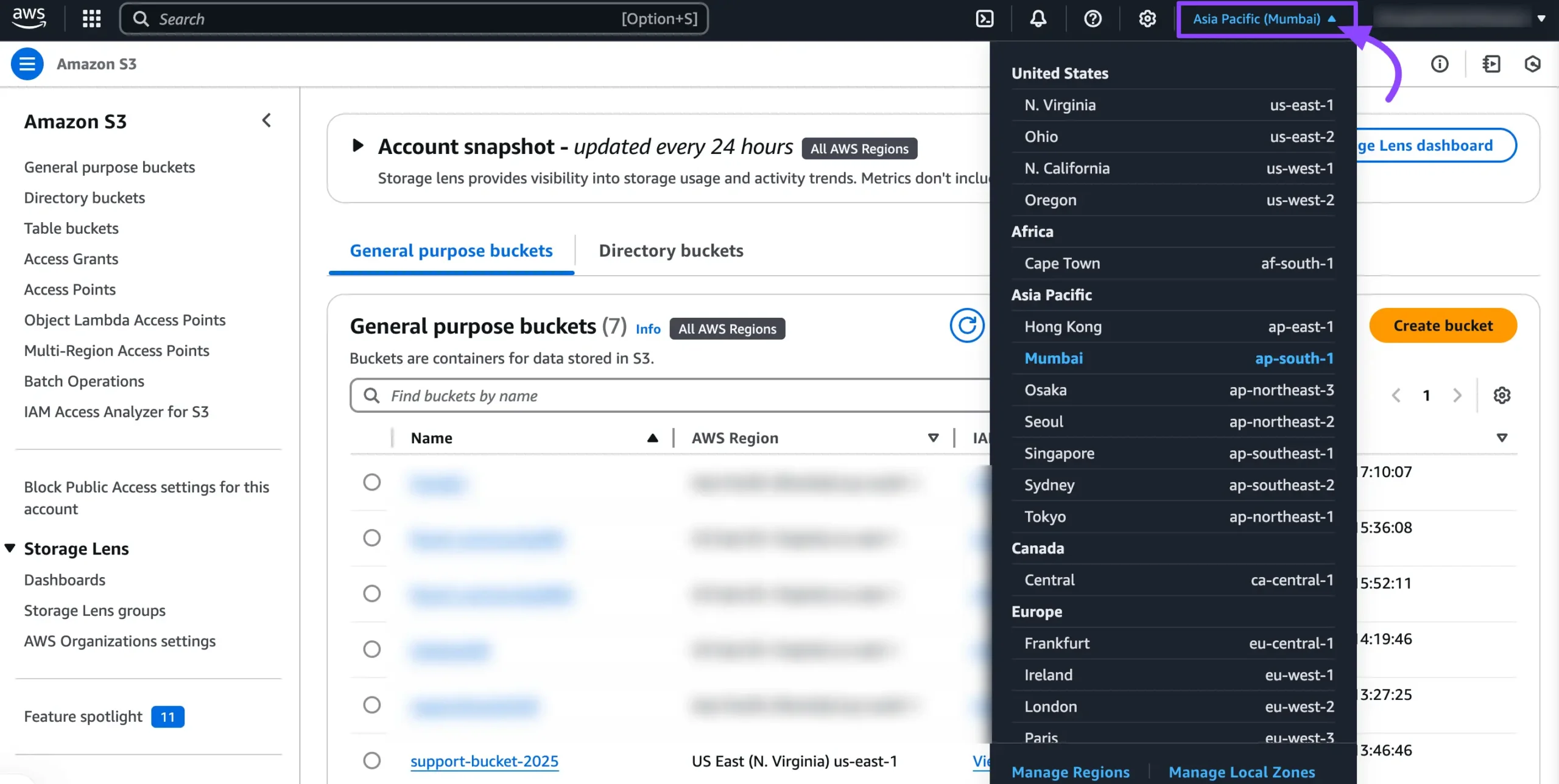
Before creating your bucket, you’ll need to choose a region. Each S3 bucket is linked to a specific region, and picking the right one can help your site load faster, lower your storage costs, and make sure you’re meeting any data regulations.
For example, if you’re located in Europe, it’s a good idea to go with a region like EU (Ireland) or EU (Frankfurt) for better performance.
To choose your region, just click on the Region name at the top of your AWS console. Then, pick your preferred region from the drop-down menu.
If you’re not sure which one to select, you can check the full list on Amazon’s official Regions and Endpoints page.
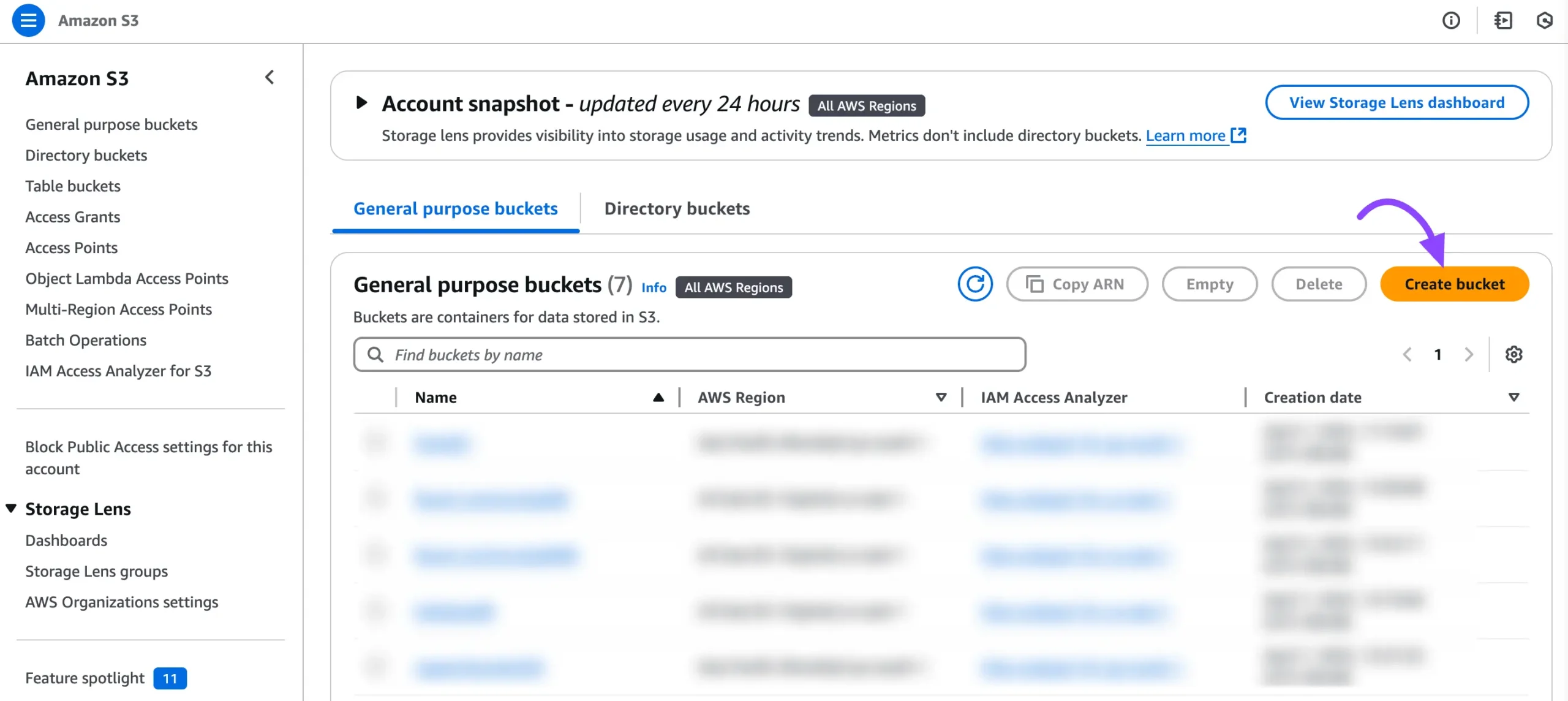
After that, create a bucket where all your FluentBoards media files will be stored. To do this, simply click the Create Bucket button. This will start the setup process for your new storage bucket.
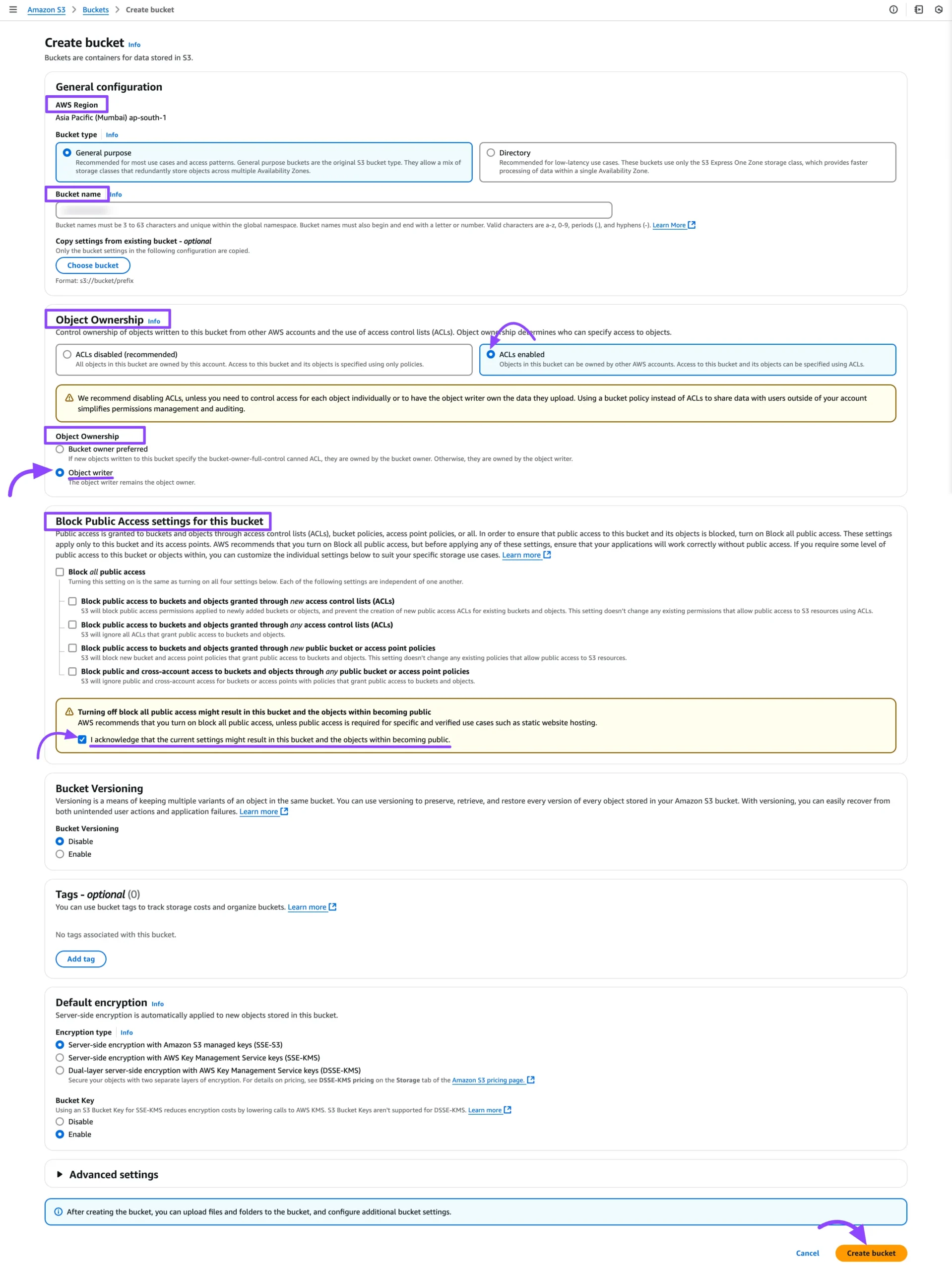
Now you will be redirected to a new page. Next, fill out the form and set up the right form permissions-
- AWS Region: Make sure the region matches the one you selected earlier.
- Bucket Name: Enter a unique name for your bucket.
- Object Ownership: Select the ACLs enabled. Then choose Object writer under Object Ownership.
- Block Public Access Settings for this Bucket: Disable the Block all public access option. Check the box saying I acknowledge that the current settings might result in this bucket and the objects within becoming public.
- Other Settings: You can customize them based on your needs or keep the defaults.
Finally, click the Create Bucket button to complete the process.
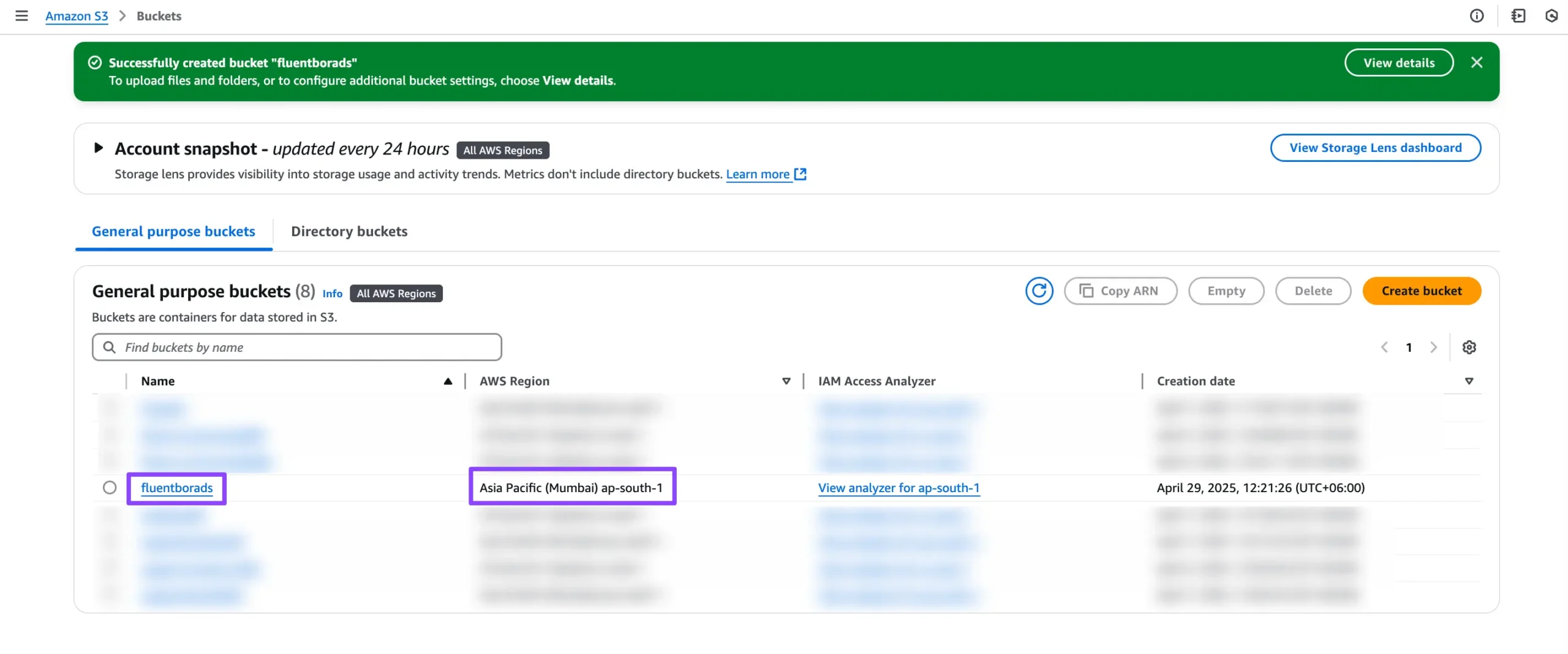
Once your bucket is successfully created, you’ll see a confirmation message, and the bucket will appear in your list.
Make sure to copy the Bucket Name and Region—you’ll need these to fill in the Bucket Name and Location fields in your FluentBoards settings.
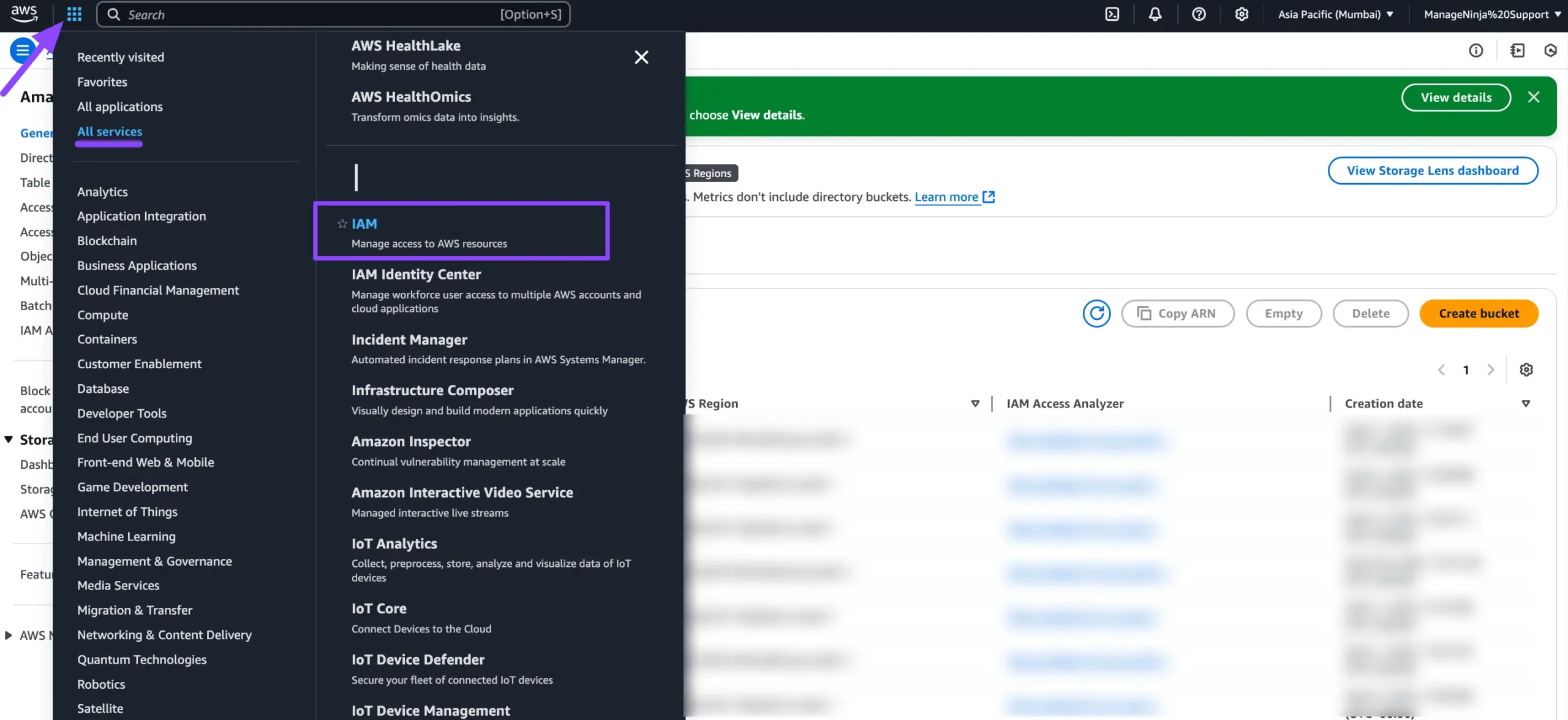
Creating IAM User for Access #
Click the All Services dropdown in the AWS navbar or search for IAM. Select IAM to begin creating a new IAM user for access.
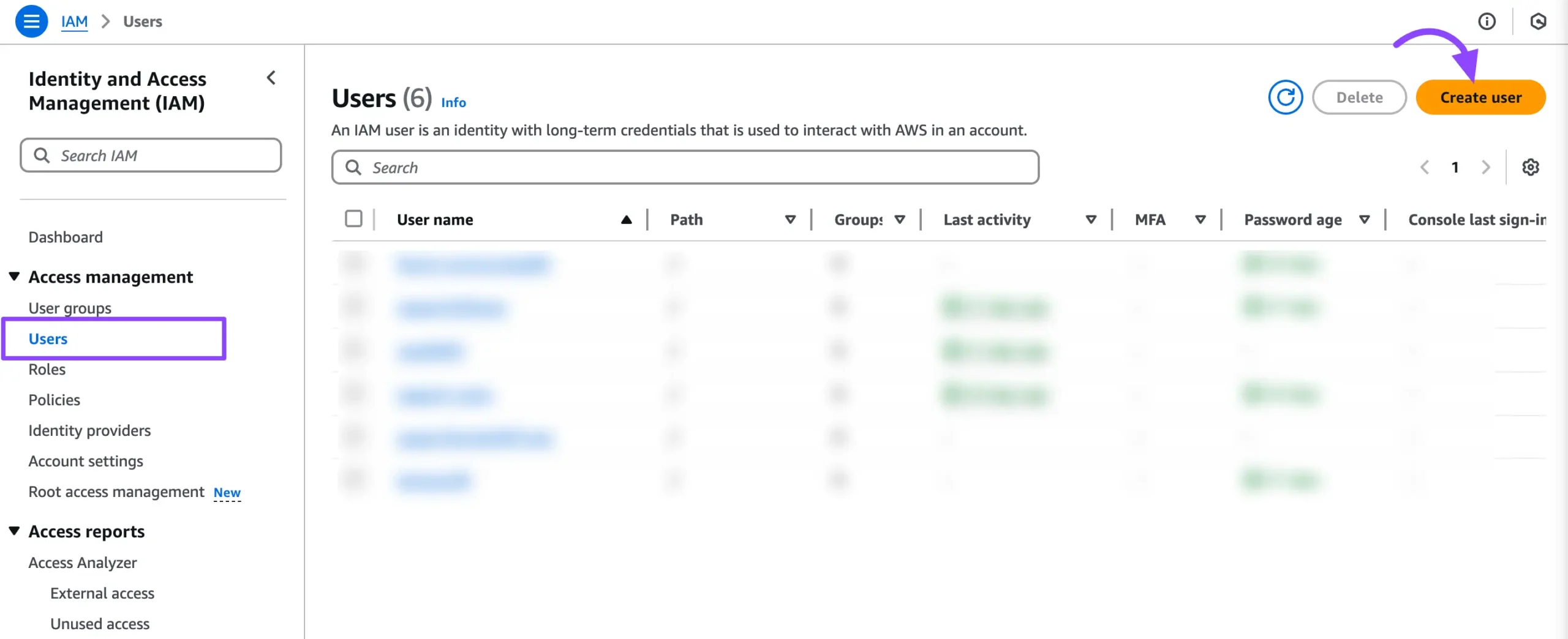
Once you’re on the IAM dashboard, click Users from the left sidebar under Access management. Next, click the Create User button to create a new IAM user.
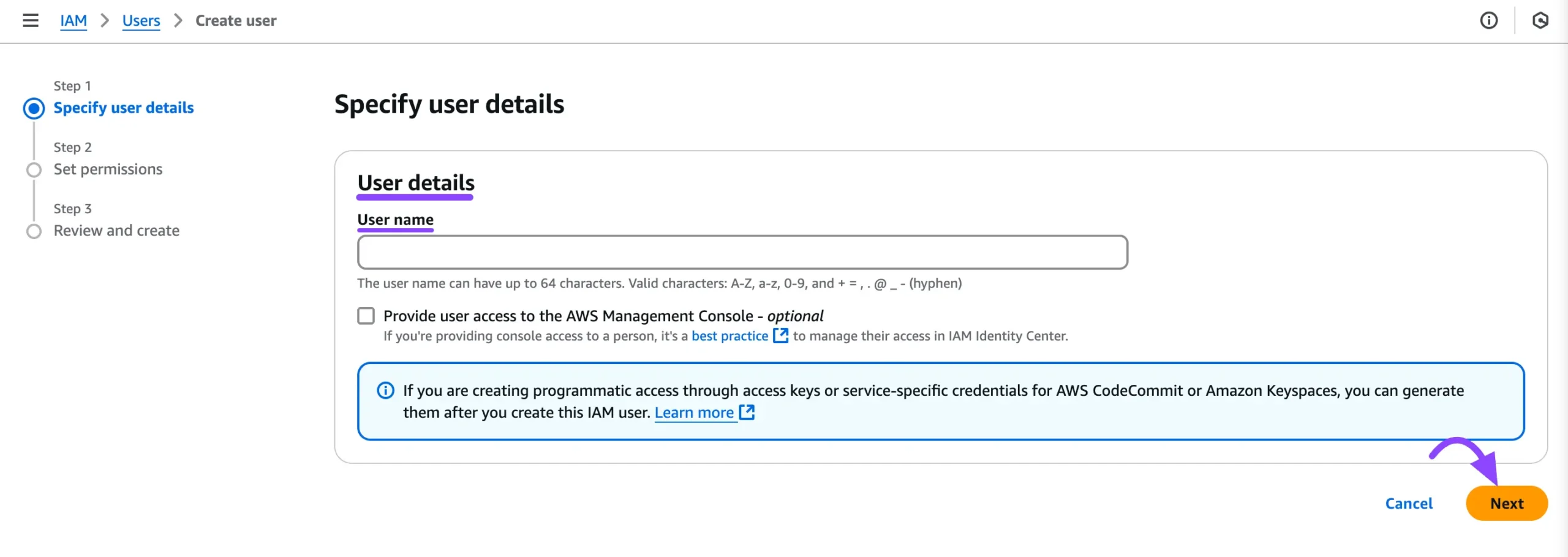
Here, enter your desired User name. Next, leave the Provide user access to the AWS Management Console (optional) option unchecked, as it’s not needed for FluentBoards integration.
Then, click the Next button to proceed to the permissions setup.
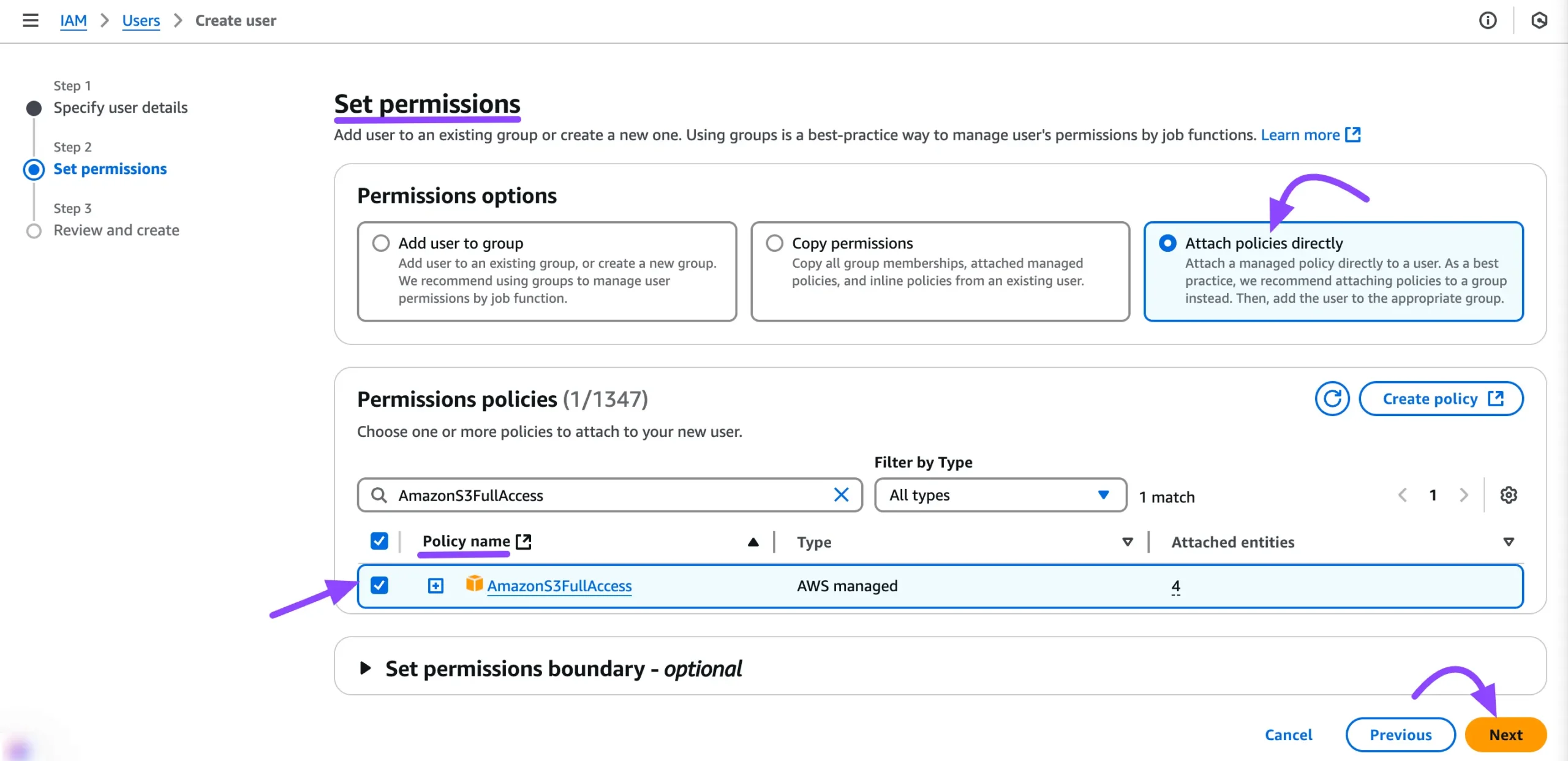
In the Set Permissions step, select Attach policies directly. Then, search for AmazonS3FullAccess in the search bar, select the policy name, and click the Next button to proceed.
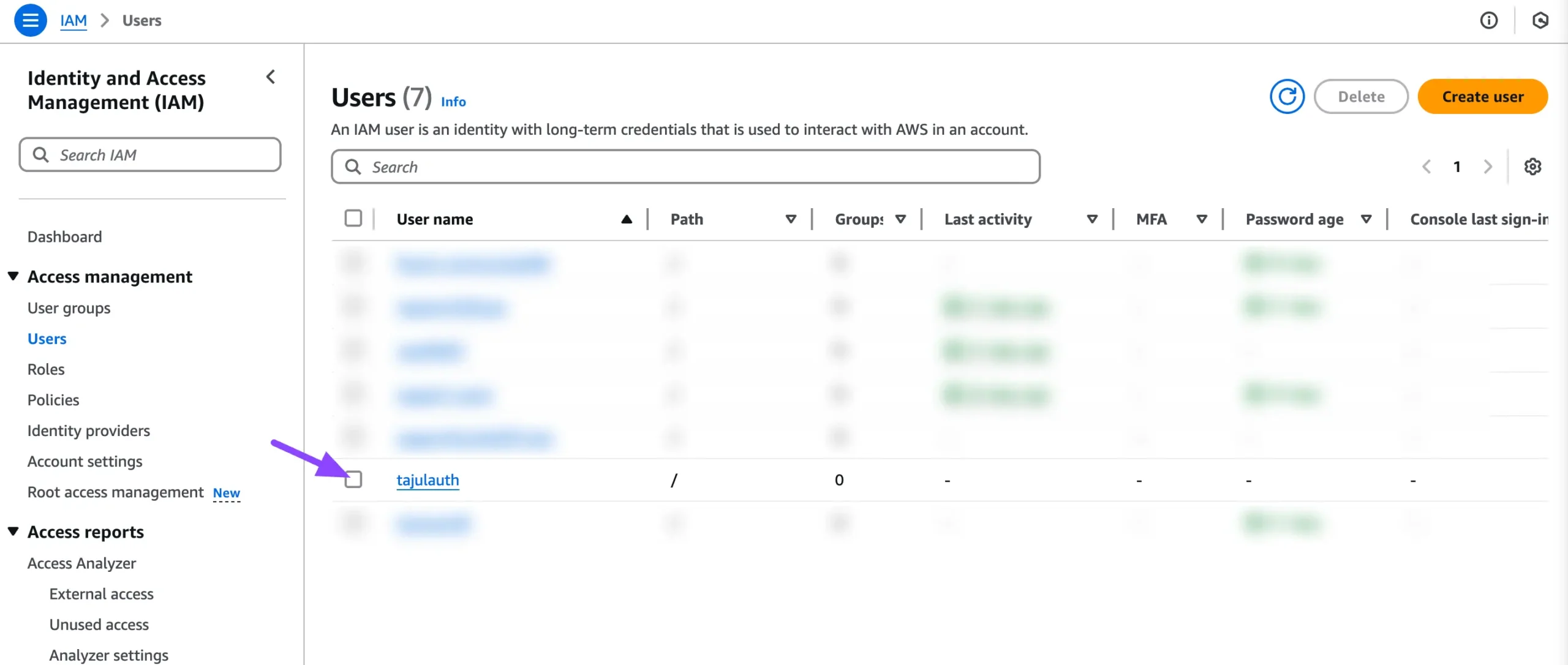
You can skip the Review and Create step and click the Create User button to create the new user.
Your user has been created successfully. In the Users section, you will now see the newly created user. Click on the User Name to view the details.
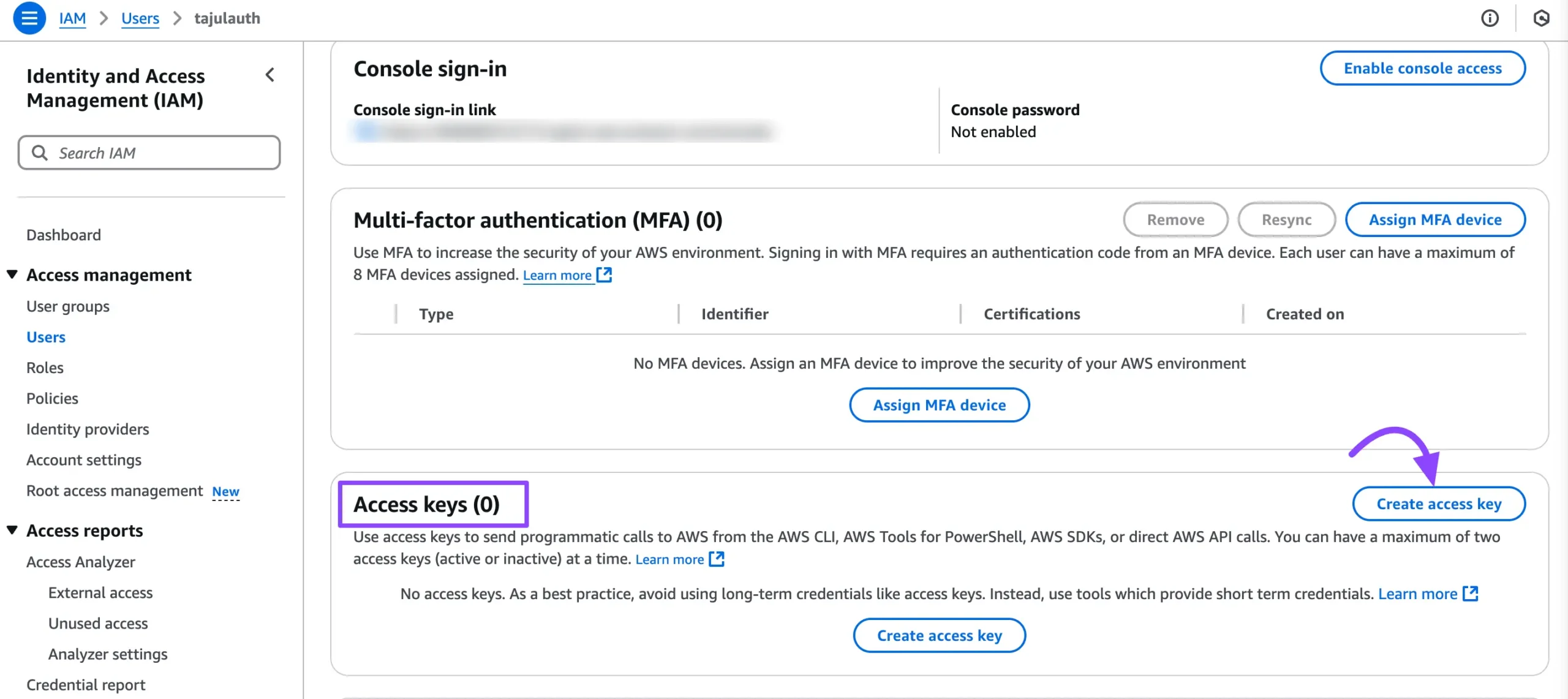
Go to the Security Credentials tab from the User Details page. Here, you will find the Access Keys section. Click the Create Access Key button to generate new access credentials for the user.
The steps to create Access Keys will appear. In the Access key best practices & Aaternatives step, select the Other option and click on the Next button to proceed.
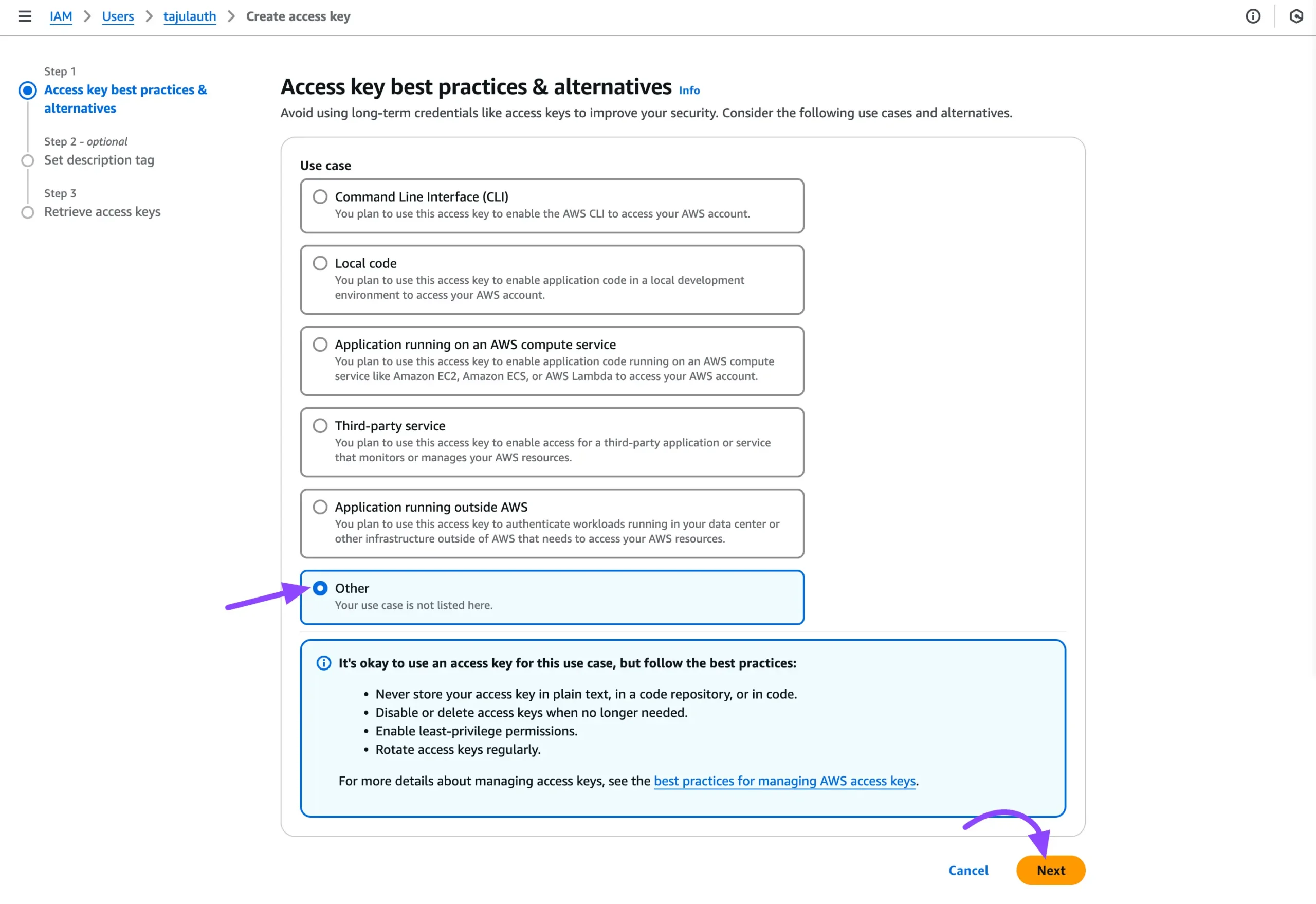
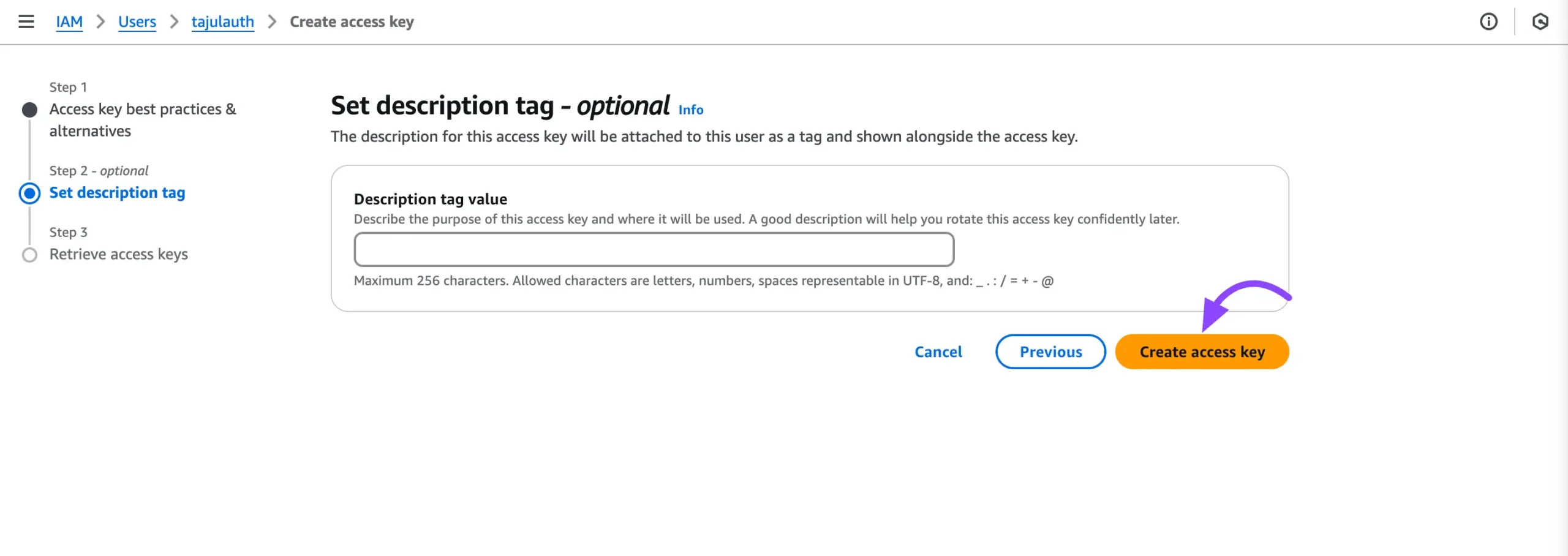
You can easily skip this step and click the Create access key button to generate the access key.
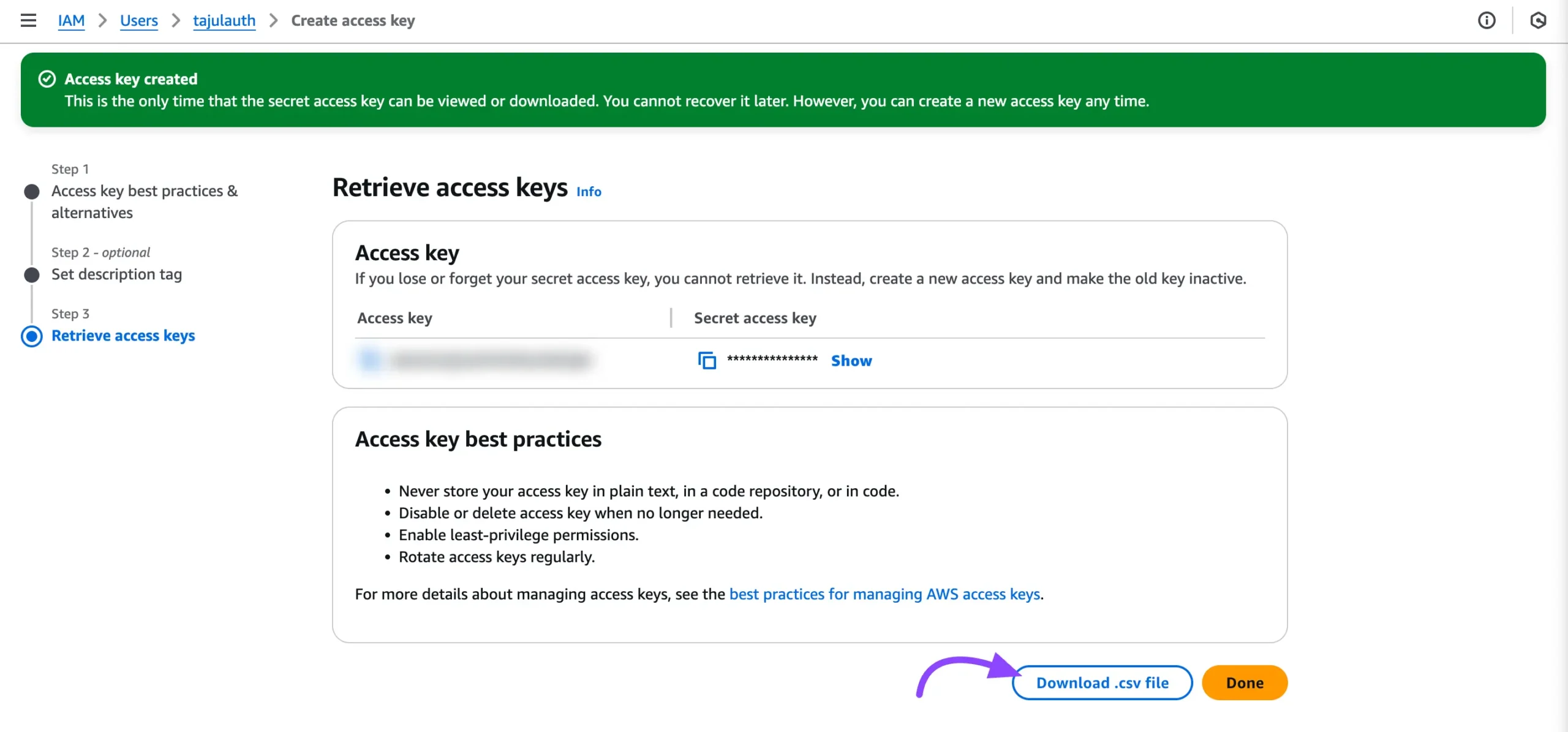
Your access key has been created successfully. Now you can see the Access Key and Secret Key here. Copy these credentials to your clipboard for later use or download them as a CSV file by clicking on the Download .csv file button.
Configure the FluentBoards with Amazon S3 #
There are two ways to configure FluentBoards with Amazon S3: Using the plugin UI or Using wp-config.php file.
Using the Plugin UI #
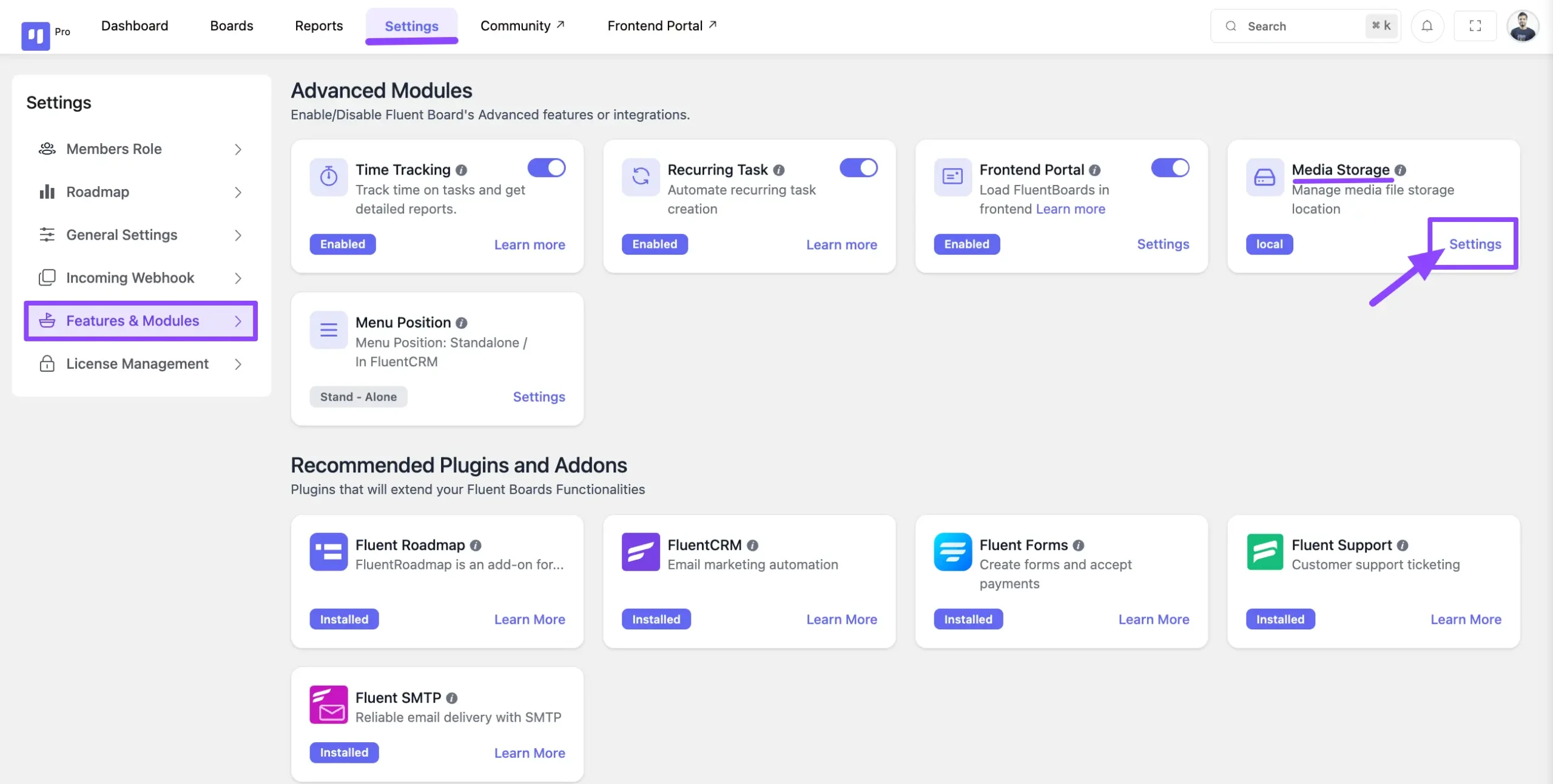
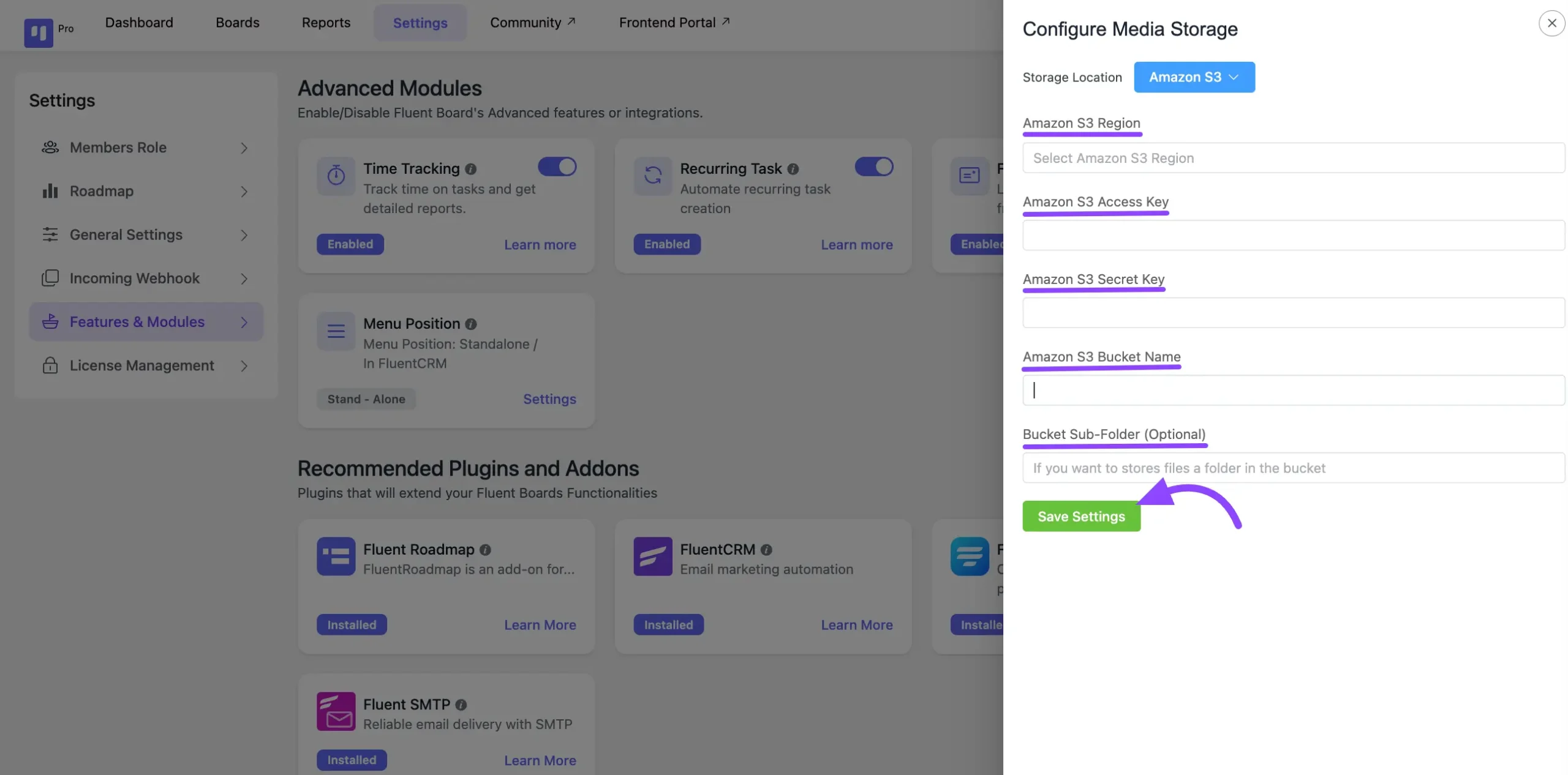
Go to FluentBoards dashboards Settings tab from the top menu. Click the Feature & Modules section from the left side bar. Now find the Media Storage and click the Settings.
After that, a popup will appear here. Now, select Amazon S3 and paste the credentials you collected from your Amazon AWS account:
- Amazon S3 Region: Select the region from the dropdown that matches the one you used when creating your bucket.
- Amazon S3 Access Key: Paste the Access Key from the IAM User.
- Amazon S3 Secret Key: Paste the Secret Key from the IAM User.
- Amazon S3 Bucket Name: Enter the Bucket Name you created in Amazon S3.
- Bucket Sub Folder (Optional): If you created a subfolder for file uploads, provide its name. Otherwise, leave it empty.
Finally, click the Save Settings button. Your Amazon S3 will now be successfully connected with FluentBoards, and all media files will be stored in Amazon S3.
Using wp-config.php file #
Add the following definitions to your wp-config.php file, adjusting the values according to your Amazon S3 setup.
```php
// Amazon S3 Configuration
define('FLUENT_BOARDS_CLOUD_STORAGE', 'amazon_s3');
define('FLUENT_BOARDS_CLOUD_STORAGE_REGION', 'your-region'); // us-east-1
define('FLUENT_BOARDS_CLOUD_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY', '********************');
define('FLUENT_BOARDS_CLOUD_STORAGE_SECRET_KEY', '********************');
define('FLUENT_BOARDS_CLOUD_STORAGE_BUCKET', 'your-bucket-name'); // change with your bucket name
define('FLUENT_BOARDS_CLOUD_STORAGE_SUB_FOLDER', 'site-name'); // optional
```Replace the placeholder values with your actual Amazon S3 credentials and information.
Troubleshooting #
- If you encounter permission issues, review your bucket policy and IAM user permissions.
- Ensure that your S3 bucket is in the correct region and that it’s accessible from your WordPress server.
- Check that your access key and secret key are entered correctly without any extra spaces.
If you have any further questions, concerns, or suggestions, please do not hesitate to contact our support team. Thank you.